 |
Indotco InternationalIt's a personal service. |
|
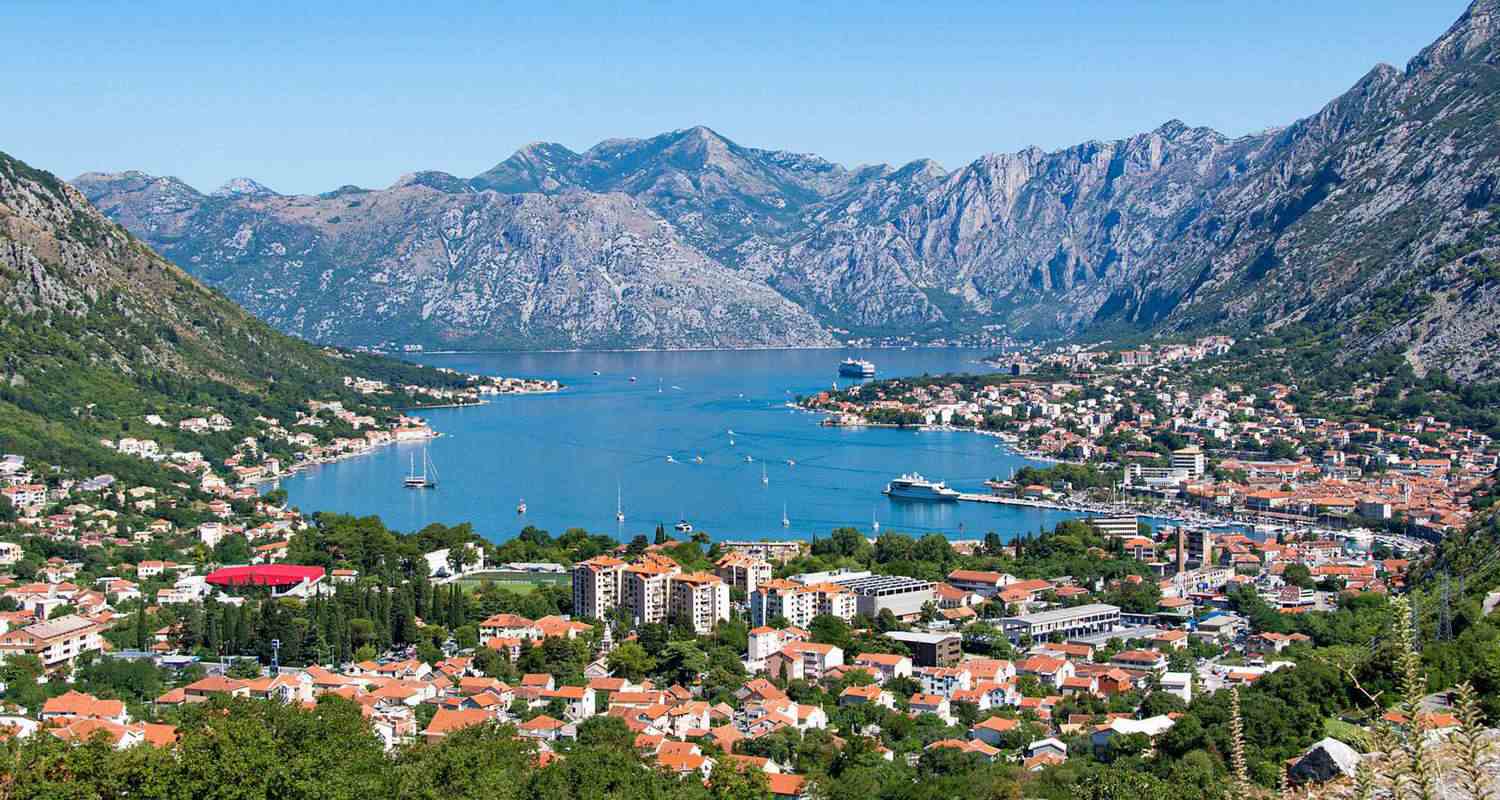

About Montenegro
Montenegro, which means "Black Mountain", is a country located in Southeast Europe on the Adriatic Sea. It is bounded by the Adriatic Sea and Croatia (southwest), Bosnia and Herzegovina (northwest), Serbia (northeast), Kosovo (east), and Albania (southeast). Montenegro’s administrative capital is Podgorica, though its cultural centre is the historical capital and older city of Cetinje. For much of the 20th century Montenegro was a part of Yugoslavia, and from 2003 to 2006 it was a component of the federated union of Serbia and Montenegro. Here are some key facts and highlights about Montenegro:
Geography - Location: Southeastern Europe, Balkan Peninsula - Borders: Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Kosovo, and Albania - Capital and Largest City: Podgorica - Area: Approximately 13,812 square kilometers (5,333 square miles) - Landscape: Known for its diverse terrain including rugged mountains, medieval villages, and a narrow strip of beaches along its Adriatic coastline. Climate Montenegro’s lower areas have a Mediterranean climate, with dry summers and mild, rainy winters. Temperature varies greatly with elevation. Podgorica, lying near sea level, is noted for having the warmest July temperatures in the country, averaging 27 °C. Cetinje, in the Karst region at an elevation of 670 metres, has an average temperature that is 5 °C lower. Average January temperatures range from 8 °C at Bar on the southern coast to −3 °C in the northern mountains. History - Ancient Times: The area now known as Montenegro was part of various ancient Illyrian and Roman territories. - Medieval Period: Became a prominent principality in the Middle Ages. The name "Montenegro" means "Black Mountain," derived from the dark forests that cover the mountain ranges. - Ottoman Rule: The region was under Ottoman rule for centuries, though parts of Montenegro maintained a degree of independence. - Modern Era: Gained independence from the Ottoman Empire in the 19th century. After World War I, it became part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. - Recent History: Montenegro was part of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and later the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. In 2006 Montenegro's parliament declared independence from the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. In 2008, the new country applied for EU membership. In 2010, the Commission issued a favourable opinion on Montenegro's application, identifying 7 key priorities that would need to be addressed for negotiations to begin, and the Council granted it candidate status. In December 2011, the Council launched the accession process with a view to opening negotiations in June 2012. The accession negotiations with Montenegro started on 29 June 2012. Montenegro is one of nine current EU candidate countries, together with Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Moldova, North Macedonia, Serbia, Turkey, and Ukraine. Chief negotiator Predrag Zenović named accession by 2028 as realistic. Montenegrin Prime Minister Milojko Spajić is optimistic that his country will conclude the vetting process for EU membership in 2026 and has previously expressed confidence that Montenegro will become the EUs 28th member by January 2028, exactly two decades after beginning its application process. The European Commission said in November 2025 that the EU could welcome new members as early as 2030 as it praised Montenegro for their progress on reforms needed to join the bloc. Culture - Language: Montenegrin (official), also widely spoken are Serbian, Bosnian, Albanian, and Croatian. - Religion: Predominantly Eastern Orthodox Christianity, with a significant number of Muslims and smaller numbers of Catholics. - Cultural Heritage: Rich in cultural heritage with numerous medieval monasteries, churches, and historic sites. Economy - Currency: Euro (EUR), even though Montenegro is not a member of the Eurozone. - Key Industries: Tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing. The Adriatic coast is a major attraction, with destinations like Kotor, Budva, and the Bay of Kotor drawing tourists worldwide. - Tourism: Plays a crucial role in the economy with its natural beauty, historic towns, and seaside resorts. The unemployment rate in Montenegro is currently 9.54% as of November 2025, having increased from 9.33% in October 2025. This rate reflects a slight rise compared to previous months, indicating ongoing labor market conditions in the country. As of December 2025, Montenegro's annual inflation rate is 4%, down from 4.2% in November 2025. This marks the lowest reading since May 2025, with prices moderating in various categories, including transport and food and non-alcoholic beverages. The most significant categories in the consumer price index include food and non-alcoholic beverages (34% of total weight), housing and utilities (15%), and transport (11%). The government anticipates a slowdown of average inflation to 2.9% on average in 2025-2027 Politics - Government: Unitary parliamentary republic - Current President: Jakov Milatović (as of 2024) - Current Prime Minister: Milojko Spajić (as of 2024) - Membership: Member of the United Nations, NATO, and a candidate for membership in the European Union. Notable Places - Kotor: A coastal town with a well-preserved medieval old town, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. - Budva: Known for its beaches, nightlife, and historic old town. - Durmitor National Park: Famous for its stunning mountainous scenery, canyons, and the Tara River Canyon. Montenegro is known for its scenic beauty, blending coastal charm with mountainous landscapes, making it a unique and attractive destination in the Balkans. Established in 1993, the Central Bank of Montenegro is responsible for monetary policy, the development of a sound banking system, and payment operations. The German mark was declared the sole means of payment in Montenegro in November 2000, and in 2002 Montenegro’s official currency became the euro, the EU’s single currency. A stock market began operating in 1996. Most enterprises in Montenegro have begun privatization, and it is expected that most of these will eventually trade on the exchange. Doing business in Montenegro offers various opportunities and challenges. The country's strategic location, developing economy, and EU candidacy make it an appealing prospect for investors. Here’s an overview of the business environment in Montenegro: Economic Overview - Currency: Euro (EUR) - GDP Growth: Montenegro has experienced moderate economic growth, driven primarily by tourism, energy, and construction sectors. - Key Industries: Tourism, energy, agriculture, and manufacturing. Business Environment - Ease of Doing Business: Montenegro is considered relatively business-friendly, with efforts to simplify administrative procedures and attract foreign investment. According to the World Bank's Doing Business report, Montenegro has made significant strides in improving its business climate. - Foreign Investment: The government encourages foreign investment and has established favorable conditions, including tax incentives and a liberal investment regime. - Taxation: Corporate tax rate is 9%, one of the lowest in Europe. VAT is 21%. Key Sectors for Investment 1. Tourism: The tourism sector is a major economic driver, with numerous opportunities in hotel development, resorts, and tourism-related services. 2. Energy: Montenegro has significant potential in renewable energy, particularly in hydropower, solar, and wind energy. 3. Real Estate: There is a growing market for real estate development, particularly along the coast and in urban centers. 4. Agriculture: Investment opportunities exist in organic farming, wine production, and other agricultural products. 5. Infrastructure: Ongoing projects to improve infrastructure, including road networks, ports, and airports, present various investment opportunities. Challenges - Regulatory Environment: While improvements have been made, bureaucratic inefficiencies and regulatory inconsistencies can pose challenges. - Corruption: Corruption remains a concern, although efforts are being made to combat it. - Small Market: The domestic market is relatively small, which can limit growth prospects for certain businesses. Steps to Start a Business 1. Business Registration: Registering a business involves submitting necessary documents to the Central Register of Business Entities. 2. Legal Structure: Common types of legal entities include limited liability companies (DOO), joint-stock companies (AD), and partnerships. 3. Permits and Licenses: Depending on the business type, specific permits and licenses may be required. 4. Bank Account: Opening a bank account in Montenegro is necessary for business transactions. 5. Tax Registration: Businesses must register with the tax authorities and obtain a tax identification number. Support for Businesses - Investment Promotion Agency: The Montenegrin Investment Promotion Agency (MIPA) provides support to investors, including information on investment opportunities and assistance with administrative procedures. - Chambers of Commerce: The Chamber of Economy of Montenegro offers networking opportunities, business advice, and support services for businesses operating in Montenegro. - Financial Support: Various grants and funding opportunities are available for businesses, particularly in key sectors like tourism and energy. Notable Business Events - Adriatic Fair: An important trade fair in Budva that attracts international exhibitors and visitors. - Montenegro Business Conference: A platform for discussing economic policies, business opportunities, and networking with potential partners. Conclusion Montenegro offers a conducive environment for business, particularly in sectors like tourism, energy, and real estate. While there are challenges, the country’s strategic location, favorable tax regime, and ongoing efforts to improve the business climate make it a promising destination for investors. You have some more questions? Contact us for a free quote. |